What is a Sentence?
Def: According to the Oxford Dictionary: A group of words containing a subject and a verb that expresses a statement, a question, etc. When a sentence is written, it begins with a big (capital) letter and ends with a full stop.
In Simple words: A sentence is a group of words with complete meaning.
Examples:
- Jack is playing outside.
- Alexa and Joy had invited me.
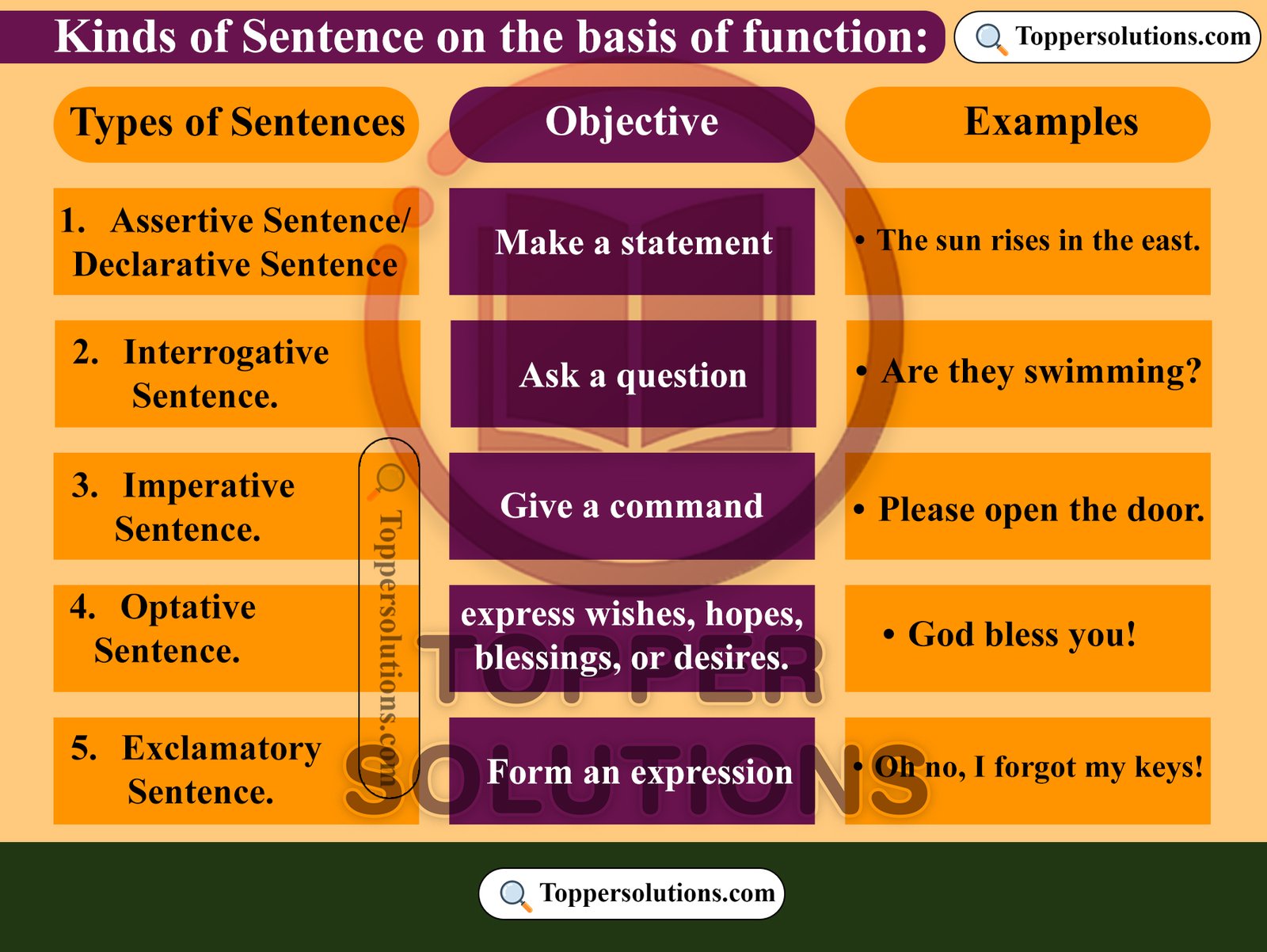
Kinds of Sentence based on function:
- Assertive Sentence/Declarative Sentence
- Interrogative Sentence.
- Imperative Sentence.
- Optative Sentence.
- Exclamatory Sentence.
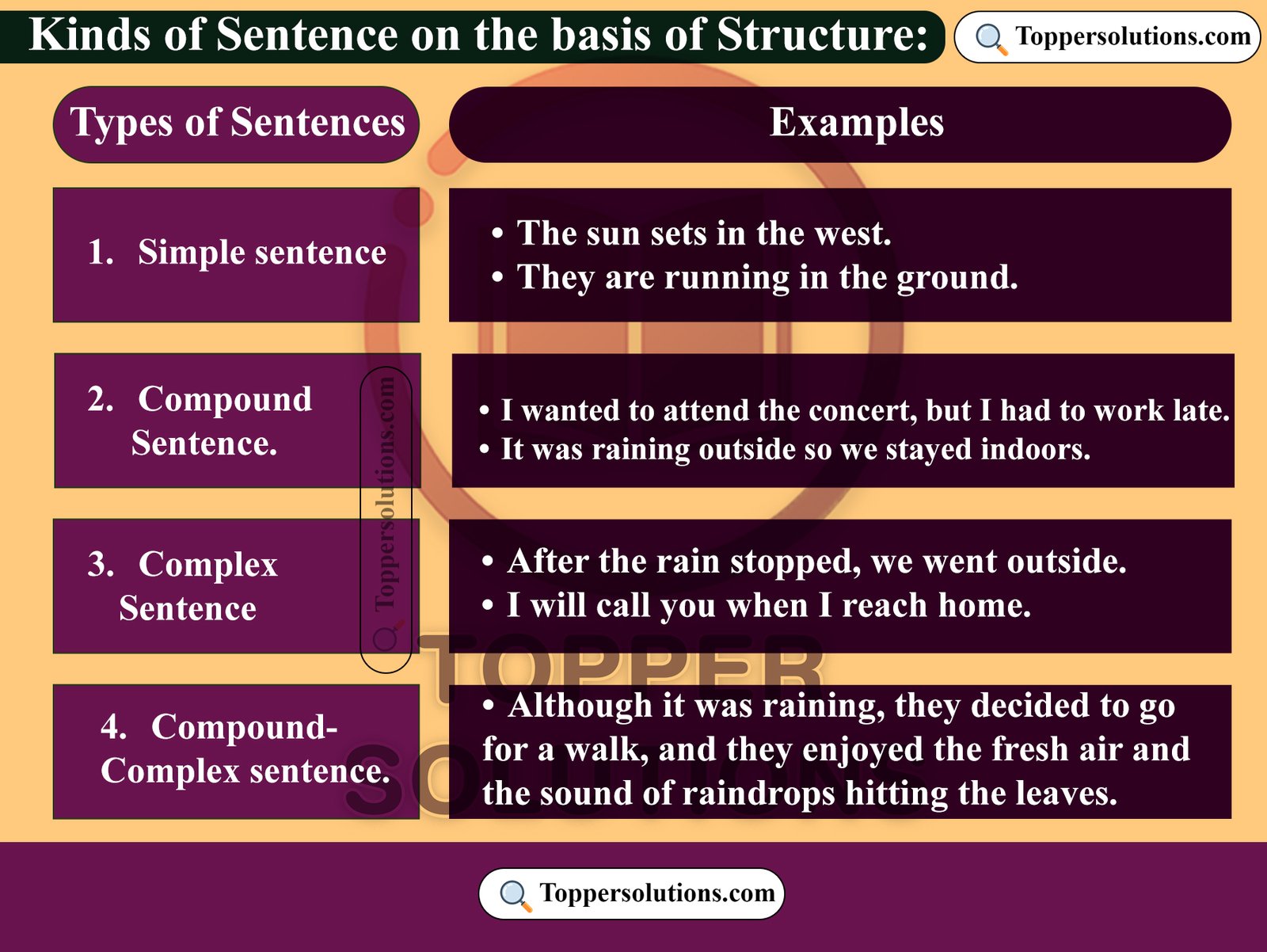
Kinds of Sentence based on structure:
- Simple sentence
- Compound Sentence.
- Complex sentence
- Compound-Complex sentence.
>>Now we will go through them one by one.
Kinds of Sentence on the basis of function:
Assertive Sentence/Declarative Sentence:
Def: Assertive Sentence or Declarative Sentence provides information or conveys a fact and typically ends with a period.
What is the main purpose of the Declarative Sentence?
The main purpose of an assertive sentence is to declare something or assert a particular idea.
Examples of Assertive Sentence or Declarative Sentence
- The sun rises in the east.
- They have finished their project.
- Elephants are the largest land animals.
- I enjoy reading books.
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- The Earth revolves around the sun.
- The star shines at night.
Interrogative Sentence.
Def: An interrogative sentence is a type of sentence that is used to ask a question. It seeks information, clarification, or confirmation. It ends with a question marks.
There are two types of Interrogative Sentences;
- Close Ended
- Open Ended
1. Close Ended:
Def: The sentence start with helping verb called close ended Question. It requires a brief answers. We generally answer it in “yes/no”.
Examples:
- Do you like to play football?
- Are they swimming?
- Have you ever visited Mumbai?
- Can you give me this chair?
2. Open Ended:
Def: The sentence start with Wh word called Open Ended Question. It is a type of question that invites a more extensive or detailed response. It cannot be answered with a simple ‘yes’ or ‘no’. It requires respondents to elaborate on their point.
Examples:
- Why are you weeping?
- When did you meet my sister?
- How have you handle this problem?
- Who killed him?
Examples of Interrogative Sentences.
- Where is the nearest library?
- What time does the train depart?
- Why did you choose that particular restaurant?
- How did you learn to play the guitar so well?
- Who is going to accompany you to the event?
- When is the deadline for submitting the project?
- Have you ever visited New York City?
- Which book are you currently reading?
- Did you enjoy the concert last night?
- Is it going to rain later today?
Imperative Sentences:
Def: An imperative sentence is a type of sentence that gives a command, makes a request, or offers advice. It is structured to express a direct order or to encourage someone to do something.
Examples of Imperative Sentences:
- Take your medicine properly.
- Please open the door.
- Let me play.
- Read the instructions carefully before answering.
- Turn off the lights when you leave the room.
- Be quiet during the exam.
Optative Sentence.
Def: An optative sentence is a type of sentence that expresses a wish, hope, cruse or desire. It generally expresses positive hopes. They are often used in blessings, greetings, or expressions of goodwill.
Examples of Optative Sentences:
- May you have a wonderful birthday!
- God bless you!
- Long live the king!
- May your dreams come true.
- Go to hell.
Exclamatory Sentence:
Def: An exclamatory sentence is a type of sentence that is used to express sudden feeling expressions.
Examples of Exclamatory Sentences:
- Alas! My cow has died.
- Hurrah! You got the first rank.
- What a delicious meal!
- Oh no, I forgot my keys!
Kinds of Sentence on the basis of Structure:
Simple Sentence:
Def: A simple sentence is a type of sentence structure that consists of just one independent clause, which contains a subject and a predicate. It expresses a complete thought and stands alone as a complete sentence.
Examples of Simple Sentences:
- The cat is sleeping.
- She sings beautifully.
- I enjoy reading books.
- They play soccer every weekend.
- The sun sets in the west.
- They are running in the ground.
Compound Sentences:
Def: A compound sentence is a type of sentence that consists of two or more independent clauses joined together by coordinating conjunctions (such as and, but, or, nor, for, yet, so) or by punctuation marks like semicolons. The independent clauses in a compound sentence are of equal importance.
Examples of Compound Sentences:
- I wanted to attend the concert, but I had to work late.
- She enjoys playing the piano, and her brother favors the guitar.
- It was raining outside so we stayed indoors.
- He finished his homework early, yet he did not get a decent night’s sleep.
- You can attend the party or stay at home.
Complex Sentences:
Def: A complex sentence is a sentence that contains one independent clause (a complete thought) and at least one dependent clause (a fragment that cannot stand alone). Complex sentences use subordinating conjunctions or relative pronouns to connect the clauses.
Examples of complex sentences:
- After the rain stopped, we went outside.
Independent clause: “We went outside”
Dependent clause: “After the rain stopped”
- Although she was tired, she continued working on her assignment.
Independent clause: “She continued working on her assignment”
Dependent clause: “Although she was tired”
- Because he missed the bus, he arrived late to the meeting.
Independent clause: “He arrived late to the meeting”
Dependent clause: “Because he missed the bus”
- I will call you when I reach home.
Independent clause: “I will call you”
Dependent clause: “when I reach home”
- The book that I borrowed from the library was fascinating.
Independent clause: “The book was fascinating”
Dependent clause: “that I borrowed from the library”
Compound-Complex sentence.
Def: A compound-complex sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses. This structure combines elements of both compound and complex sentences.
Examples of compound-complex sentences:
- Although it was raining, they decided to go for a walk, and they enjoyed the fresh air and the sound of raindrops hitting the leaves.
Independent clause 1: “They decided to go for a walk”
Independent clause 2: “They enjoyed the fresh air and the sound of raindrops hitting the leaves”
Dependent clause: “Although it was raining”
- She studied hard for the exam, but she couldn’t remember all the details, so she didn’t perform as well as she had hoped.
Independent clause 1: “She studied hard for the exam”
Independent clause 2: “She didn’t perform as well as she had hoped”
Dependent clause: “but she couldn’t remember all the details, so”
Examples of kinds of Sentences
- The cat sleeps on the windowsill. (Simple Sentence)
- I wanted to go to the party, but I had to finish my work. (Compound Sentence)
- Because it was raining, we stayed indoors. (Complex Sentence)
- Where is the nearest supermarket? (Interrogative Sentence)
- Please turn off the lights before leaving. (Imperative Sentence)
- May you have a happy and prosperous New Year! (Optative Sentence)
- How fast the horse is running! (Exclamatory Sentence)
- Although she was tired, she continued working, and when she finished, she went to bed. (Compound-Complex Sentence)
6 thoughts on “What is a sentence: Definition, types and examples:”