Tense Chart; Tense in English
What is a Tense Chart?
Tense Chart
A tense chart is a visual representation of various actions occurring at various points of time. It has various types of tenses organized into a table format which provides a clear overview of the various forms of verbs used to indicate different time frames in which an action takes place.
What is Tense?
A tense is a form of the verb that allows you to express time. The tense of the verb tells us when an event or something existed or when a person did something. Past, present, and future are the three main types of tenses.
According to Oxford Dictionary, “Tense is any of the forms of a verb that may be used to show the time of the action or situation expressed by the verb”.
According to Merriam-Webster Dictionary, “The term tense means a distinction of form in a verb to express distinctions of time or duration of the action or state it denotes”.
According to Collins Dictionary, “Tense is defined as any of the forms of a verb which reveal the time at which an action has happened”.
According to Cambridge Dictionary “tense” is “any of the forms of a verb which show the time at which an action happened.”
According to the Britannica Dictionary “a form of a verb that is used to show when an action happened”
Types of Tense
In English Grammar, tenses are of three types, that is,
- Present Tense
- Past Tense
- Future Tense
Further, it consists of four forms:
- Simple
- Perfect
- Continuous
- Perfect Continuous
So, in total there are 12 tenses which are as follows:
| Tenses | Tenses forms |
| Present Tense | Simple Present Tense |
| Present Perfect Tense | |
| Present Continuous Tense | |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| Past tense | Simple Past Tense |
| Past Perfect Tense | |
| Past Continuous Tense | |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| Future Tense | Simple Future Tense |
| Future Perfect Tense | |
| Future Continuous Tense | |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense |
Below is the table of the examples of tenses-
| Tense | Forms | Examples |
| Present Tense | Simple Present Tense | He drives a car |
| Present Perfect Tense | He is driving a car | |
| Present Continuous Tense | He has driven a car | |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | He has been driving a car since morning | |
| Past Tense | Simple Past Tense | He drove a car |
| Past Perfect Tense | He was driving a car | |
| Past Continuous Tense | He had driven a car | |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | He had been driving the car since 7 am | |
| Future Tense | Simple Future Tense | He will drive a car |
| Future Perfect Tense | He will be driving a car | |
| Future Continuous Tense | He will have driven a car | |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | He will have been driving the car at 6 am tomorrow |
Significance of Tense Chart
A tense chart is a visual representation of various actions occurring at various points of time. It has various types of tenses organised into a table format which provides a clear overview of the various forms of verbs used to indicate different time frames in which an action takes place.
Tense Chart with Rules and Examples
| Tense Chart | ||
| Tenses | Rules and Formula | Examples |
| Simple Present Tense | Subject + V1 / III person plural form + other words | Seema invites me to every party. |
| Present Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping Verb(am/is/are) + ing form (v4) + other words | They are playing chess. |
| Present perfect tense | Subject + Helping Verb (have/has) + III form of verb + other words | They have started a new company. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + Have/Has + Been + ing form (V4) + other words + since/for + time. | I have been working on this project for a week. |
| Simple Past Tense | Subject + 2nd form of verb/verb in the past tense + other words | Sneha went to the market last night. |
| Past Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping Verb(was/were) + Main verb + ing + other words | It was raining today today. |
| Past Perfect Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (had) + Past participle of the main verb + other words | The patient had died before the doctor came. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + Had + Been + Verb + ing + other words + since/for + time. | She has been cleaning the room since 9 o’clock |
| Simple Future Tense | Subject + will/shall + V1 + Object | I will finish my breakfast |
| Future Continuous | Subject + will be/shall be + V1 + ing + Object | I will have been waiting for my mom |
| Future Perfect Tense | Subject + will have/shall have + V3 + Object | I will have dressed up by the time you reach home. |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + will have been + V1 + ing + Object + since/for + time. | They will have been waiting for me. |
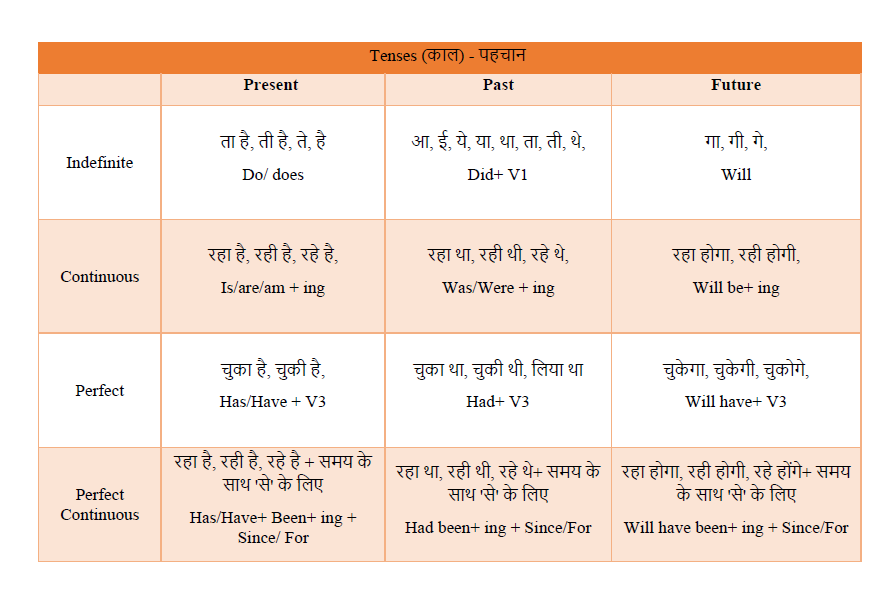
Tense Chart In Hindi
Tense (काल) क्रिया का वह स्वरूप है जो किसी कार्य या घटना के समय और उस कार्य या घटना की दशा को बताता है। मुख़्यता काल तीन प्रकार के होते है, वर्त्तमान काल , भुतकाल, भविष्यकाल । काल के कितने प्रकार होते है, वर्त्तमानकाल के भेद, भुतकाल के भेद, भविष्यकाल के भेद विस्तार में नीचे दिए हुए है।
|
Tenses (काल) – पहचान |
|||
| Present | Past | Future | |
| Indefinite | ता है, ती है, ते, है
Do/ does |
आ, ई, ये, या, था, ता, ती, थे,
Did+ V1 |
गा, गी, गे,
Will |
| Continuous | रहा है, रही है, रहे है,
Is/are/am + ing |
रहा था, रही थी, रहे थे,
Was/Were + ing |
रहा होगा, रही होगी,
Will be+ ing |
| Perfect | चुका है, चुकी है,
Has/Have + V3 |
चुका था, चुकी थी, लिया था
Had+ V3 |
चुकेगा, चुकेगी, चुकोगे,
Will have+ V3 |
| Perfect Continuous | रहा है, रही है, रहे है + समय के साथ ‘से’ के लिए
Has/Have+ Been+ ing + Since/ For |
रहा था, रही थी, रहे थे+ समय के साथ ‘से’ के लिए
Had been+ ing + Since/For |
रहा होगा, रही होगी, रहे होंगे+ समय के साथ ‘से’ के लिए
Will have been+ ing + Since/For |
-
Present Tense
Definition: The present tense is the verb form you use when you talk about what’s happening right now. “You are standing on my foot” is in the present tense.
Below is the tense chart of the Present Tense.
Types of Present Tense
In English Grammar, there are four types of the present tense, these are:
- Simple Present Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
-
Simple Present Tense:
When the verb defines/denotes an activity that is going on in the present time or is a regular event, then the verb is used in a simple present tense form.
Basic Formulas for Simple Present Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Main verb (V1) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (Do/Does) + not + Main verb (V1) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(Do/Does) + Subject + Main verb (V1) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(Do/Does) + Subject + not + Main verb (V1) + object?
Note: There are two types of interrogative sentences.
- Open Ended Questions.
- Close-ended questions.
1. Open Ended Questions.
Open-ended questions are broad and can be answered in detail.
e.g.
i. What do you think about this product?
ii. Which is the best country in the world?
- Close-ended questions.
Closed-ended questions are narrow in focus and usually answered with a single word or a pick from limited multiple-choice options
e.g.
i. Are you satisfied with this product?
ii. Do you want to see this picture?
→ Yes/No/Mostly/Not quite
Simple Present Tense Examples:
- I work in London.
- She works in London.
- I’m nineteen years old. …
- I play football every weekend.
- The human body contains 206 bones. …
- I sometimes go to the cinema. …
- The school term starts next week.
- Do you play the piano?
- Where do you live?
- Does Jack play football?
- Where does he come from?
- Do Rita and Angela live in Manchester?
- Where do they work?
-
Present Continuous Tense:
When the verb defines or denotes the action or condition that is happening now and continues till the future, then such verb is used as Present Continuous Tense.
The basic formula for Present Continuous Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (is/are/am) + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (is/are/am) + not + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(is/are/am) + Subject + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(is/are/am) + Subject + not + Main verb (V4) + object?
Present Continuous Tense Examples:
- Children are going to school.
- The boys are playing in the park.
- The baby is crying out loud.
- It is raining now.
- I am cooking pasta for lunch.
- Miss Peters is teaching the class.
- Are you listening?
- Are they coming to your party?
- When is she going home?
- What am I doing here?
- Present Perfect Tense: When the verb defines or denotes the past action in the present form, then such verb is used as Present Perfect Tense.
The Basic Formulas for Present Perfect Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (has/have) + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (has/have) + not + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(has/have) + Subject + Main verb (V3) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(has/have) + Subject + not + Main verb (V3) + object?
Present Perfect Tense Example
- Raj has just gone out to the market.
- The clock has just struck twelve.
- We have gone for a walk.
- Toby has eaten all the cookies.
- My mother has cut her finger.
- I have I’ve seen that film before.
- I’ve played the guitar ever since I was a teenager.
- I can’t get in the house. I’ve lost my keys.
- Teresa isn’t at home. I think she has gone shopping.
- He has written three books and he is working on another one. done all my homework.
- I have been in Pune for one week
-
Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
When the verb defines or denotes the action that shows that something started in the past and is continuing at present, then such verb is used as Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
The Basic Formulas for Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (has/have) + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (has/have) + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(has/have) + Subject + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(has/have) + Subject + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Examples:
- Max has been visiting Turkey regularly for the last few years.
- Alisha has visited Turkey before, but it’s been a while.
- The family has not been skiing this winter.
- I haven’t been socializing very much lately.
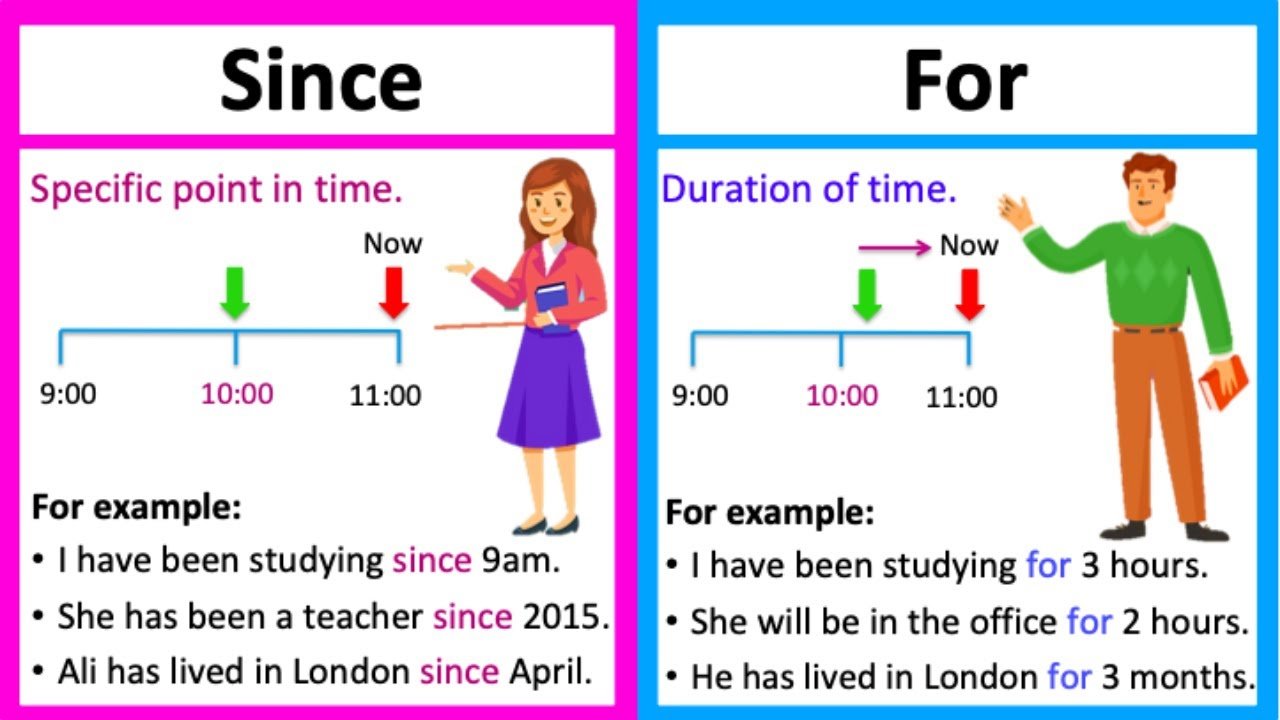
Use of Since and for
Past Tense
The past tense refers to the action or event that has already occurred or has taken place in the past. It refers to the activity that has already happened. It can also be defined as the form of the verb which expresses the action or state of action that happened in the past. Below is the tense chart of Past Tense.
Types of Past Tense
In English Grammar, there are four types of past tense, these are:
- Simple Past Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
-
Simple Past Tense:
When the verb defines/denotes an activity that is used to indicate an action or event that happened in the past.
The Basic Formulas for Simple Past Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Main verb (V2) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (Did) + not + Main verb (V1) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(Did) + Subject + Main verb (V1) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(did) + Subject + not + Main verb (V1) + object?
Simple Past Tense Examples:
- John Cabot sailed to America in 1498.
- My father died last year.
- He lived in Fiji in 1976.
- We crossed the Channel yesterday.
- We went to the park yesterday evening.
- I forgot about the meeting.
- Manu opened the door for the guests.
-
Past Continuous Tense:
When the verb defines/denotes an activity that is used to depict an action or event that was continuing in the past, then such verb is used as Past Continuous Tense.
The Basic Formulas for Past Continuous Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (was/were) + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (was/were) + not + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(was/were) + Subject + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(was/were) + Subject + not + Main verb (V4) + object?
Past Continuous Tense Examples:
- It was snowing yesterday.
- They were eating at the restaurant.
- You were working yesterday.
- I was studying last night.
- I was waiting for the cab when I met Raj.
- The children were shouting when the teacher came in.
- It was midnight when it was raining.
- Everyone was clapping.
- It was snowing today.
- They were eating at the dhaba.
- You were working tomorrow.
- I was studying last night.
- I was waiting for the cab when I met Usha.
- The students were shouting when the teacher came in.
- It was midnight when it was raining.
- Everyone was clapping.
3. Past Perfect Tense:
When the verb defines/denotes an activity that is used to represent an event or action that happened in the past before another event or action that happened in the past, then such verb is used as a Past Perfect Tense.
The Basic Formulas for Past Perfect Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (had) + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (had) + not + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(had) + Subject + Main verb (V3) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(had) + Subject + not + Main verb (V3) + object?
Past Perfect Tense Examples:
- I had finished the work. …
- I had been working there for a year. …
- When George died, he and Anne had been married for nearly fifty years. …
- She didn’t want to move. …
- He was a wonderful guitarist. …
- My eighteenth birthday was the worst day I had ever had. …
- I couldn’t get into the house.
-
Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
This verb form is used to define/denotes used to denote an action or event that was taking place in the past until another action or event happened in the past.
The Basic Formulas For Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (had + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (had) + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(had) + Subject + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh /Helping Verb (had) + Subject + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense Examples:
- Had you been waiting long before the taxi arrived?
- We had been trying to open the door for five minutes when Jane found her key.
- It had been raining hard for several hours and the streets were very wet.
- Her friends had been thinking of calling the police when she walked in.
Future Tense
The ‘future tense’ form of any verb refers to the change of the verb form to represent an action that is going to happen in the future or will be continuing in the future.
Types of Future Tense
In English, there are four types of the future tense:
- Simple Future Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
-
Simple Future Tense:
The change in verb form which is used to denote/ defines an action that will happen in the future, then the verb is used as simple future tense.
Basic Formula for Simple Future Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + helping verb (will/shall) Main verb (V1) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall) + not + Main verb (V1) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb (will/shall) + Subject + Main verb (V1) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb (will/shall) + Subject + not + Main verb (V1) + object?
Simple Future Tense Examples:
- I will meet him later.
- You will come.
- It will rain tomorrow.
- She will be late.
- He will help us later.
- We will get married in September.
- They will cook dinner.
- We will go shopping in that market this Monday.
-
Future Continuous Tense:
The change in verb form is used to denote/define those actions that will be in progress/motion at some point in the future.
The Basic Formulas for Future Continuous Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall + be) + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall) + not + be + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(will/shall) + Subject + be + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(will/shall ) + Subject + not + be + Main verb (V4) + object?
Future Continuous Tense Examples:
- I will be writing the letter tomorrow.
- The baby will be playing the whole night.
- I will be helping my mother to make breakfast.
- Sheldon will be eating the cake later.
- Penny will be running the marathon tomorrow.
- She will be taking her dog for a walk.
-
Future Perfect Tense:
The change in verb for in which is used to indicate an action that will be taking place in the future.
Basic Formula For Future Perfect Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall have) + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall) + not + have + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(will/shall) + Subject + have + Main verb (V3) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(will/shall) + Subject + not + have + Main verb (V3) + object?
Future Perfect Tense Examples:
- I will have been here for six months on June 23rd.
- By the time you read this I will have left.
- You will have finished your report by this time next week.
- Won’t they have arrived by 5:00?
- Will you have eaten when I pick you up?
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
The verb form denotes/defines a verb tense that describes actions that will continue up until a point in the future.
The Basic Formulas for Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (had + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (had) + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(had) + Subject + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh /Helping Verb (had) + Subject + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
Future Perfect Continuous Tense Examples:
- I will have been waiting here for three hours by six o’clock.
- By 2006 I will have been living in London for sixteen years.
- When I finish this course, I will have been learning English for twenty years.
- I will have been waiting here for three hours by six o’clock.
- By 2001 I will have been living in London for sixteen years.
- When I finish this course, I will have been learning English for twenty years.
- Next year I will have been working here for four years.
- Next year I will have been working here for four years.
- When I come at 6:00, will you have been practicing long?
4 thoughts on “Tense Chart; Tense in English”