Active and Passive Voice
Voice (Active and Passive Voice)
Transitive verbs have both active and passive forms:
There are two types of voice
- Active: Subject acts.
- Passive: An object receives the action.
Compare:
Ram writes a letter. (Active voice) A letter is written by Ram. (Passive voice)
Note: These two sentences express the same meaning.
Why do we need a passive voice?
Ans. The passive voice allows speakers and writers not to mention an “agent,” especially when information about the agent is unknown, unimportant, obvious, confidential, or difficult to identify. (The word “agent” refers to the performer of an action.)
How to change Active Voice into Passive Voice:
- The Subject is changed into Passive Voice.
- An object is changed into a Subject.
- Always the third form of the verb is used.
- A suitable preposition is used before the Subject.
- Tenses and Pronouns are changed as per the rule.
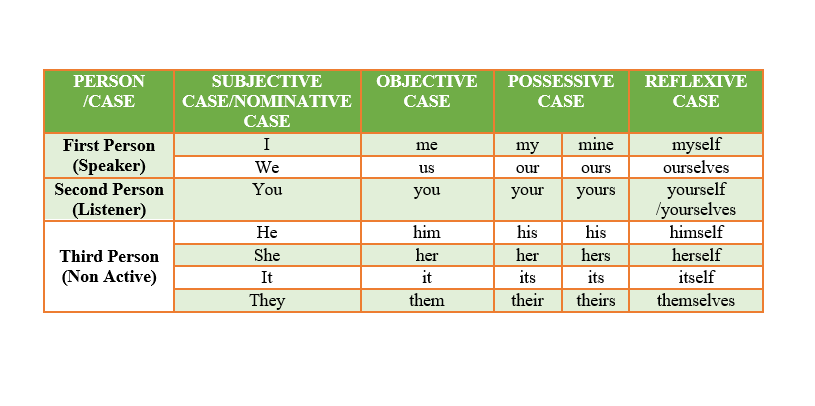
Table 1: Pronoun Table:
| PERSON /CASE | SUBJECTIVE CASE/NOMINATIVE CASE | OBJECTIVE CASE | POSSESSIVE CASE | REFLEXIVE CASE | |
| First Person
(Speaker) |
I | me | my | mine | myself |
| We | us | our | ours | ourselves | |
| Second Person
(Listener) |
You | you | your | yours | yourself
/yourselves |
| Third Person
(Non-Active) |
He | him | his | his | himself |
| She | her | her | hers | herself | |
| It | it | its | its | itself | |
| They | them | their | theirs | themselves | |
Table 2: Tense Table
Trick:
- Simple Tense →Continuous
- Continuous Tense → Continuous
- Perfect Tense → Perfect Continuous Tense
| Active Voice | Passive Voice | |
| Simple | Simple Present Tense (Affirmative) | Present Continuous Tense(Affirmative) |
| Subject + Verb-I + Object. | Object + is/are/am + Verb – III + by + Subject. | |
| Simple Present Tense (Negative) | Present Continuous Tense (Negative) | |
| Subject + H.V (does/do) + Verb-I + Object. | Object + is/are/am + not + Verb – III + by + Subject. | |
| Simple Past Tense (Affirmative) | Past Continuous Tense (Affirmative) | |
| Subject + Verb-II + Object. | Object + was/were + Verb – III + by + Subject. | |
| Simple Past Tense (Negative) | Past Continuous Tense (Negative) | |
| Subject + H.V (did) + Verb-I + Object. | Object + was/were + not + Verb – III + by + Subject. | |
| Simple Future Tense (Affirmative) | Future Continuous Tense(Affirmative) | |
| Subject + H.V (will/shall) + Verb-I + Object. | Object + will/shall + Verb – III + by + Subject. | |
| Continuous | Present Continuous Tense | Present Continuous Tense |
| Sub + H.V (is/are/am) + V – 4/(ing) + Object | Object + is/are/am + being+ Verb – III + by + Subject. | |
| Past Continuous Tense | Past Continuous Tense | |
| Sub + H.V (was/were) + V – 4/(ing) + Object | Object + was/were + being+ Verb – III + by + Subject. | |
| Future Continuous | No change | |
| Perfect | Present Perfect Tense | Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
| Sub + H.V (has/have) + V-III + Object | Object + H.V (has/have) + been + V-III + by + Subject. | |
| Past Perfect Tense | Past Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| Sub + H.V (had) + V-III + Object | Object + H.V (had) + been + V-III + by + Subject. | |
| Future Perfect Tense | Future Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| Sub + H.V (will/shall + have) + V-III + Object | Object + H.V (will/shall + have) + been + V-III + by + Subject. |
Note: The sentence contains be/been, and does not form a passive voice. i.e. (Present perfect continuous/ Past Perfect Continuous/ Future Perfect Continuous/ Future Continuous)
Table: III (Examples)
| Active Voice | Passive Voice | |
| Simple | Simple Present Tense (Affirmative) | Present Continuous Tense(Affirmative) |
| I write a letter. | A letter is written by me. | |
| Simple Present Tense (Negative) | Present Continuous Tense (Negative) | |
| I do not write a letter. | A letter is not written by me. | |
| Simple Past Tense (Affirmative) | Past Continuous Tense (Affirmative) | |
| I wrote a letter | A letter was written by me. | |
| Simple Past Tense (Negative) | Past Continuous Tense (Negative) | |
| I did not write a letter. | A letter was not written by me. | |
| Simple Future Tense (Affirmative) | Future Continuous Tense(Affirmative) | |
| I shall write a letter. | A letter will be written by me. | |
| Continuous | Present Continuous Tense | Present Continuous Tense |
| I am writing a letter. | A letter is being written by me. | |
| Past Continuous Tense | Past Continuous Tense | |
| I was writing a letter. | A letter was being written by me. | |
| Future Continuous | No change | |
| Perfect | Present Perfect Tense | Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
| I have written a letter. | A letter has been written by me. | |
| Past Perfect Tense | Past Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| I had written a letter. | A letter had been written by me. | |
| Future Perfect Tense | Future Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| I shall have written a letter. | I will have been written by me |
Some Other examples of Active Voice and Passive:
- The cat chased the mouse. (Active Voice)
The mouse was chased by the cat. (Passive Voice)
- She teaches English. (Active Voice)
English is taught by her. (Passive Voice)
- They built a sandcastle on the beach. (Active Voice)
A sandcastle was built on the beach. (Passive Voice)
- I wrote a poem for my sister. (Active Voice)
A poem was written for my sister by me. (Passive Voice)
- The chef prepared a delicious meal. (Active Voice)
A delicious meal was prepared by the chef. (Passive Voice)
- The gardener planted colorful flowers. (Active Voice)
Colorful flowers were planted by the gardener. (Passive Voice)
- The students completed the assignment. (Active Voice)
The assignment was completed by the students. (Passive Voice)
- He repaired the car. (Active Voice)
The car was repaired by him. (Passive Voice)
- She sang a beautiful song. (Active Voice)
A beautiful song was sung by her. (Passive Voice)
- The team won the championship. (Active Voice)
The championship was won by the team. (Passive Voice)
Modal Verbs
Modals Verbs: (can/could/may/might/will/shall/would/should/must/ought to/need not/used to/dare)
(Active Voice): Subject + modal + verb – I + Object.
(Passive Voice): Object + modal + be + V – III + by + Subject.
Examples of Active Voice with Modal Verbs:
- She can solve the problem.
The problem can be solved by her.
- He must finish the project.
The project must be finished by him.
- We should complete the assignment.
The assignment should be completed by us.
- They may attend the meeting.
The meeting may be attended by them.
- I will submit the report.
The report will be submitted by me.
- You ought to apologize.
Apologies ought to be made by you.
- We might visit the museum.
The museum might be visited by us.
- She can speak French.
French can be spoken by her.
- He should exercise regularly.
Regular exercise should be done by him.
- They will deliver the package.
The package will be delivered by them.
Double Objects:
There are two types of objects.
- Direct Object.
- Indirect Object.
- Direct Object: It is used for non-living thing
- Indirect Object: It is used for living thing
Example:
Mr. Raj taught us English.
They were taught English by Mr. Kumar.
- Active: Mr. Raj taught them English.
Passive: They were taught English by Mr. Raj.
or
English was taught to them by Mr. Raj.
- Active: You should teach the man a lesson.
Passive: The man should be taught a lesson by you.
- Active: The police gave him a reward of Rs. 2000/-.
Passive: He was given a reward of Rs. 1000/- by the police.
- Active: The doctor gave the child an injection.
Passive: The child was given an injection by the doctor.
- Active: My grandmother tells me stories at night.
Passive: I am told stories by my grandmother at night.
Interrogative Sentences:
There are two types of Interrogative Sentences.
- Close-ended questions.
- Open Ended Questions.
Close-ended Questions: These questions are narrow in focus and usually answered with a single word or a pick from limited multiple-choice options
E.g.
- Are you satisfied with this product?
- Do you watch TV?
→ Yes/No/Mostly/Not quite
Open-ended questions: These are broad and can be answered in detail
E.g.
- What do you think about this product?
- Why did you work there?
Examples of Active Voice with Modal Verbs:
- Active: Do the boys play cricket?
Passive: Is cricket played by the boys?
- Active: Was she cooking food in the kitchen?
Passive: Was food being cooked in the kitchen by her?
- Active: Did she write a letter to her father?
Passive: Was a letter written to her father by her?
- Active Voice: Where did you leave your keys?
Passive Voice: Where were your keys left by you?
- Active Voice: Who painted this beautiful picture?
Passive Voice: By whom was this beautiful picture painted?
- Active Voice: What did you have for breakfast this morning?
Passive Voice: What did you have for breakfast this morning by you?
- Active Voice: How did the fire start?
Passive Voice: How was the fire started?
- Active Voice: Why did the dog run away?
Passive Voice: Why was the dog run away by you?
- Active: Are you helping your sister?
Passive: Is your sister being helped by you?
10. Active: Have you finished your work?
Passive: Has your work been finished by you?
- Active: When will you return my book?
Passive: When will my book be returned by you?
- Active: Why were you laughing at Geeta?
Passive: Why was Geeta being laughed at by you?
- Active: What is he writing?
Passive: What is being written by him?
- Active: Whom do you like most?
Passive: Who is liked most by you?
- Active: Whom is she helping?
Passive: Who is being helped by her?
Interrogative Sentences start with “Who”.
Active: Who + verb + object?
Passive: By whom + helping verb + object + verb – III?
Examples:
Active – Who appreciates him?
Passive – By whom is he appreciated?
Active: Who broke this beautiful cup?
Passive: By whom was this beautiful cup broken?
Active: Who will help you in your difficulty?
Passive: By whom will you be helped in your difficulty?
Active: Who can solve this question?
Passive: By whom can this question be solved?
Interrogative Sentences start with “Whom”.
Active: Whom + verb + object?
Passive: Who + helping verb + verb – III + by + Subject?
Examples:
Active – Whom do you read?
Passive – Who is read by you?
Active – Whom doesn’t he love?
Passive – Who is not loved by him?
Active – Whom is John inviting?
Passive – Who is being invited by John?
Active – Whom are they teaching?
Passive – Who are being taught by them?
Active – Whom is not she requesting for a job?
Passive – Who is not being requested by her for a job?
or
Who is not being requested for a job by her?
Active – Whom have you cheated?
Passive – Who has been cheated by you?
Active – Whom haven’t you given the money?
Passive – Who hasn’t been given the money by you?
Active – Whom has she encouraged?
Passive – Who has been encouraged by her?
Active – Whom hasn’t she called?
Passive – Who hasn’t been called by her?
Imperative Sentence: (Positive Sentence)
- It can be started with the “first form of verb.”
- It can be started with “do not + V – I.”
- It can be started with “Please/kindly.”
Formulas:
Active – M.V – I + object.
Passive – Let + obj + be + V3 .
Or
You are ordered/requested/suggested/advised to + given sentence.
Examples:
Active – Write a letter.
Passive – Let a letter be written.
Or
You are requested to write a letter.
Active – Close the door.
Passive – Let the door be closed.
Or
You are ordered to close the door.
Active – Do your job.
Passive – Let your job be done,
Or
You are advised to do your job.
Imperative Sentence: (Negative Sentence)
Active – Do not + M.V – I + object.
Passive – Let + obj + not + be + V3.
or
You are prohibited to + given sentence.
or
You are ordered/requested/suggested/advised + not + to + given sentence.
Active – Do not pluck the flowers.
Passive – Let the flowers not be plucked.
Or
You are prohibited to pluck the flowers.
Or
You are ordered not to pluck the flowers.
Imperative Sentence: (Request) [Please/Kindly]
Formulas:
Active – Please/Kindly + M.V – I + object.
Passive – You are requested to V1 + Object.
Or
Object + may + please/kindly + be + V3.
Note: remove please/kindly.
Examples.
Active – Please give me your pen.
Passive – You are requested to give me your pen.
Or
Your pen may please be given to me.
Unimportant Subjects.
→We drop unimportant subjects while making Passive Voice.
Unimportant Subjects. (We, They, Someone, Somebody, No one, Nobody, Everyone, Everybody, All of them, All people, People, Police, one, children………)
Note: But some people and many people are not unimportant subjects.
Examples.
- Active: People take tea in the morning.
Passive: Tea is taken in the morning.
- Active: Many people take tea in the morning.
Passive: Tea is taken by many people in the morning.
- Active: They abused the leader in the meeting.
Passive: The leader was abused in the meeting.
- Active: Someone is waiting for you in the room.
Passive: You are being waited in the room.
- Active: Some people do not eat onions.
Passive: Onions are not eaten by some people.
3 thoughts on “Active and Passive Voice”