Modal Verbs
What is Modal?
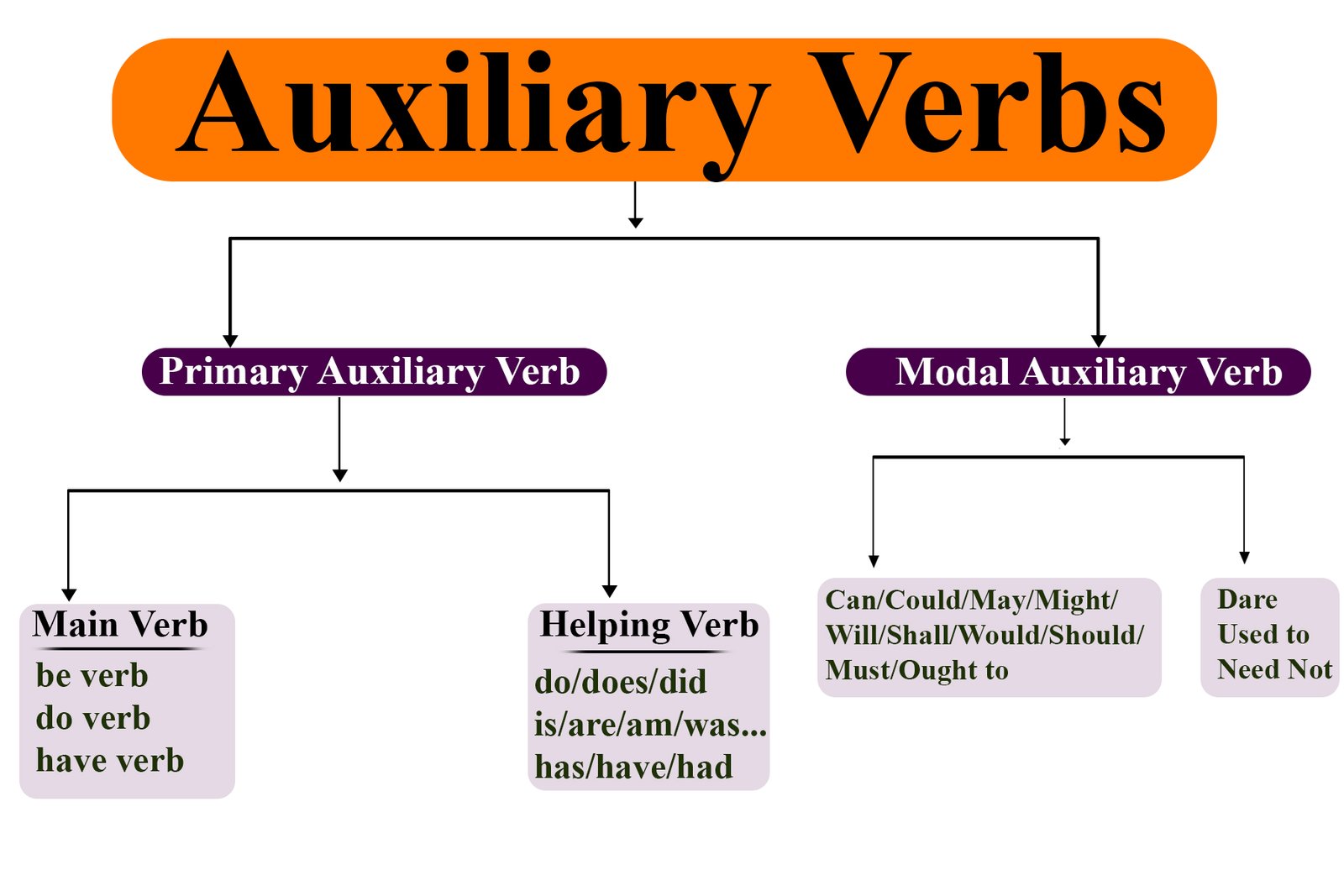
These are the Primary helping verb
- Be (is, are, am, was, were, been, being)
- Have (has, have, had)
- Do (do, does, did)
- Modals Auxiliary
Modal verbs show possibility, intent, ability, or necessity. Common examples of modal verbs include can, should, and must. Because they’re a type of auxiliary verb (helper verb), they’re used alongside the infinitive form of the main verb of a sentence. Can, could, may, might, must, will, would, shall, should, used to, need to, ought to, dare not
Modal Auxiliary
- Modals H.V. का कार्य करते हैं तथा इनके बाद MV, का प्रयोग होता है। www
- Modals पर Subject के Number (वचन). Gender (लिंग) का कोई प्रभाव नहीं पड़ता है।
- Modals के बाद not लगाने पर व्यक्य नकारात्मक बन जाता है तथा इनको वाक्य के शुरु में लगाने पर वाक्य Interrogative बन जाता है।
- Modals के बाद To (infinitive) का प्रयोग नहीं होता है। (ought to and used to को छोड़ कर)
- सामान्यतः Modal को Negative में not के साथ संक्षिप्त (contracted) रुप में लिखा जाता है। जैसे:-
- Can + not + can’t
- Shall + not = shan’t
- Must + not = mustn’t
- Could + not = couldn’t
- Will + not = won’t
- Need + not = needn’t
- May + not = mayn’t
- Would + not = wouldn’t
- Might + not = mightn’t
- Should + not = shouldn’t
- Dare + not = daren’t
Use of Modals:
1. Can का प्रयोग
Can का अर्थ है- किसी कार्य को करने की ताकत इसके द्वारा वर्तमान समय के लिए भाव जैसे- power, ability, capacity, know how to, potentiality, power, capable, intelligence, skill, strength, cleverness आदि बताये जाते हैं-
- I can learn English. (Ability)
- He can lift the box. (Capacity)
- I cannot maintain a car. (Absence of capacity)
- A dumb cannot speak. (Capacity)
- She can sing and dance. (Ability)
- He can repair a radio. (Know how to)
2. Could का प्रयोग:-
Could, Can का Past होता है। अतः इसका प्रयोग Conditional तथा Indirect Narration पाले पाक्यों में Can के Past के रुप में किया जाता है। इसके अलाश इसका प्रयोग past power/ability/capacity/know how to/potentiality, capable, intelligence, skill strength आदि के लिए किया जाता है-
- When I was young, I could lift a bag of hundred kg. (Past Capacity)
- I could speak French, when I was twenty years old. (Past Ability)
Note-साधारणतया Could का Past में प्रयोग करते है, परन्तु यह Polite Request को व्यक्त करने के लिए Present का बोध कराता है।
जैसे-
- Could you help me?
- Could you lend me 10 rupees?
3. May का प्रयोग:-
इसका प्रयोग वर्तमान व भविष्य के लिए किया जाता है। इसका प्रयोग निम्न भावों जैसे permission, possibility, probability, likely, wish, curse, bless, hope, purpose, guess, perhaps, desire, prediction आदि को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है-
- May I play here? (Permission)
- May I come in? (Permission)
- He has a car. He may be very rich. (Likelihood)
- May you live long! (Wish)
- May God forgive us! (Hope)
- We eat so that we may live. (Purpose)
- There are clouds in the sky. It may rain. (Possibility/Probability)
Note:- यदि Principal Clause Present Tense में हो तथा subordinate clause that/so that/in order that से शुरु हो तो इससे Purpose का बोच होता है अतः subordinate clause में may का प्रयोग करते हैं।
- You work hard that/so that/in order that you may pass. (Purpose)
- We read so that/in order that we may get a job. (Purpose)
- We should work hard so that we may get good job. (Purpose)
4. Might का प्रयोगः-
यह May का Past है। अतः इसका प्रयोग Conditional तथा Indirect Narration पाले वाक्यों में May के Past के रुप में किया जाता है। इसके अलावा इसका प्रयोग weak or remote possibility/probability को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है-
- He said that he might be late. (Weak possibility/probability)
- There are few clouds in the sky. It might rain today. (Remote possibility/probability)
5. Will/Shall का प्रयोग
Future Tense में will का प्रयोग II व III Person Pronouns के साथ shall का प्रयोग Person Pronouns के साथ किया जाता है। परन्तु Modals के रुप में इसके विपरीत will का प्रयोग Person Pronoun के साथ व Shall का प्रयोग III Person Pronouns के साथ किया जाता है-
Modals के रुप में Will और shall वायदा (Promise), दृढ निश्चय (Determination), धमकी (Threat), चेतावनी (Warning),इच्छा (Willingness), इरादा (Intention) आदि का भाव व्यक्त करते हैं। जैसे-
- I will help you. (Promise)
- They shall help her in the difficulty. (Promise)
- We will win the match. (Determination)
- We shall teach Pak a good lesson in the next war. (Threat)
- He shall play a match. (Determination)
- If you again abuse me, I will beat you. (Warning)
- I will kill you. (Threat)
Note: Will का प्रयोग II Person Pronoun के साथ request का भाव प्रकट करने के लिये किया जाता है-
- Will you help me?
- Will you give me hundred rupees? (Request)
6. Would का प्रयोग-
इसका प्रयोग polite request, past habit, preference को बताने के लिए किया जाता है। जैसे-
- Would you lend me your pen? (Polite request)
- You would rather take tea. (Preference)
- I would walk five kms. a day in my childhood. (Past habit)
Note:-Would, Will का Past होता है अतः इसका प्रयोग Conditional तथा Indirect narration में will के चेंज के रूप में होता है।
- If he abused me, I would beat him.
- If I were a bird. I would fly in the sky.
7. Should का प्रयोगः-
इसका प्रयोग moral duty, moral obligation, advice, suggestion को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है। जैसे-
- We should respect our teachers.
- One should keep one’s word’s. (Moral duty/Obligation)
- We should bathe daily. (Advice/Suggestion)
Note:- Should, Shall का Past होता है अतः इसका प्रयोग Conditional तथा Indirect narration में shall के past के रुप में होता है। जैसे-
- I should get good marks if the teacher taught us well.
Note:-Should, lest के बाद उद्देश्य प्रकट करता है जैसे-
- Run slow lest you should fall.
8. Ought to का प्रयोगः-
इसका प्रयोग moral duty, moral obligation को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है। जैसे-
- We ought to respect our elders. (Moral duty/Obligation)
- One ought to keep one’s promises. (Moral duty/Obligation)
- We ought not to abuse others. (Advice/Suggestion)
9. Must का प्रयोगः-
Must का अर्थ बाध्यता से होता है। यह compulsory, necessary, certain, sure, obligation duty, order, command, strong possibility/probability आदि moods को व्यक्त करता है। जैसे-
- Students must attend the class. (Compulsion)
- You must stop where you are. (Command)
- One must obey the traffic rules. (Compulsion)
- Examination are at hand. You must get up early. (Obligation)
- You must go there. (Order)
- If you get payment, you must teach in the class. (Duty)
















2 thoughts on “Modal Verbs”