Why is a tense chart important?
A tense chart is important for several reasons, particularly in the study and use of language. Tenses are grammatical categories that indicate the time when an action or a state of being occurs.
A tense chart typically organizes verb conjugations based on time, indicating when an action or state of being occurs. Here’s a basic tense chart with examples in English:

What is tense?
Answer: Tense refers to the grammatical category that expresses the time of an action or state of being in relation to the present, past, or future. It is a crucial aspect of language that helps convey when an event occurred, is occurring, or will occur.
What are the three main types of the Tense?
- Present Tense
- Past Tense
- Future Tense
Present Tense :
The present tense is a grammatical category that expresses actions or states of being that are happening now or are generally true. It is used to describe events that are occurring at the present moment, habitual actions, or facts that are always true.
Examples:
- I play football.
- She is watching TV.
- They have done their homework.
- He has been drawing a picture for an hour.
Past Tense:
The past tense is a grammatical category that indicates actions, events, or states that have already occurred or were completed in the past. It is used to describe and reference situations that happened before the present moment.
Examples:
- She needed a pen.
- I was closing my bank account.
- You had made a big mistake.
- Keats had been writing a novel for 3 months.
Future Tense
The future tense is a grammatical category that indicates actions, events, or states that will occur after the present moment. It is used to express what is expected, planned, or predicted to happen in the future.
Examples:
- We shall work for you.
- He will attend the meeting.
- Raman will be playing cricket.
- Shakira will have typed a message.
- It will have been travelling for 10 minutes
What are the three sub types of the Tense?
⇒Every tense is divided into four sub parts?
- Simple Tense
- Continuous Tense
- Perfect Tense
- Perfect Continuous Tense
Simple Present Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Main verb (V1) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (Do/Does) + not + Main verb (V1) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(Do/Does) + Subject + Main verb (V1) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(Do/Does) + Subject + not + Main verb (V1) + object?
Present Continuous Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (is/are/am) + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (is/are/am) + not + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(is/are/am) + Subject + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(is/are/am) + Subject + not + Main verb (V4) + object?
Present Perfect Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (has/have) + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (has/have) + not + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(has/have) + Subject + Main verb (V3) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(has/have) + Subject + not + Main verb (V3) + object?
Present Perfect Continuous Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (has/have) + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (has/have) + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(has/have) + Subject + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(has/have) + Subject + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
Simple Past Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Main verb (V2) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (Did) + not + Main verb (V1) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(Did) + Subject + Main verb (V1) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(did) + Subject + not + Main verb (V1) + object?
Past Continuous Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (was/were) + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (was/were) + not + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(was/were) + Subject + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(was/were) + Subject + not + Main verb (V4) + object?
Past Perfect Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (had) + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (had) + not + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(had) + Subject + Main verb (V3) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(had) + Subject + not + Main verb (V3) + object?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (had + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (had) + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(had) + Subject + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh /Helping Verb (had) + Subject + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
Simple Future Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + helping verb (will/shall) Main verb (V1) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall) + not + Main verb (V1) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb (will/shall) + Subject + Main verb (V1) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb (will/shall) + Subject + not + Main verb (V1) + object?
Future Continuous Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall + be) + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall) + not + be + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(will/shall) + Subject + be + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(will/shall ) + Subject + not + be + Main verb (V4) + object?
Future Perfect Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall have) + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (will/shall) + not + have + Main verb (V3) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(will/shall) + Subject + have + Main verb (V3) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh/Helping Verb(will/shall) + Subject + not + have + Main verb (V3) + object?
Future Perfect Continuous Tense formulas:
- Affirmative: Subject + Helping Verb (had + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Negative: Subject + Helping Verb (had) + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object.
- Interrogative: Wh/Helping Verb(had) + Subject + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
- Interrogative Negative: Wh /Helping Verb (had) + Subject + not + been + Main verb (V4) + object?
A tense chart with a singular subject is important for several reasons, particularly in the context of language learning and effective communication
Here is the another chart of the Tense
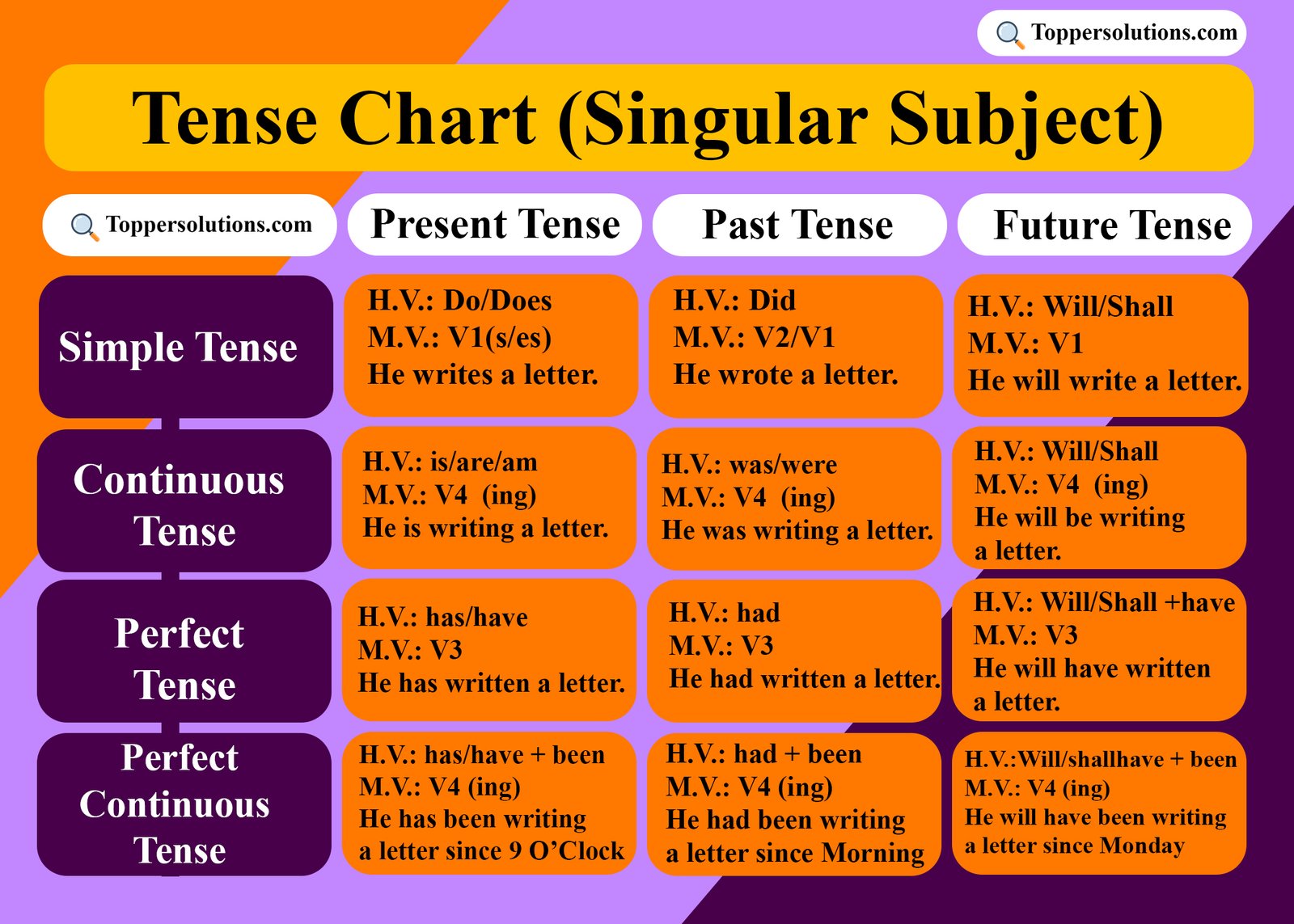
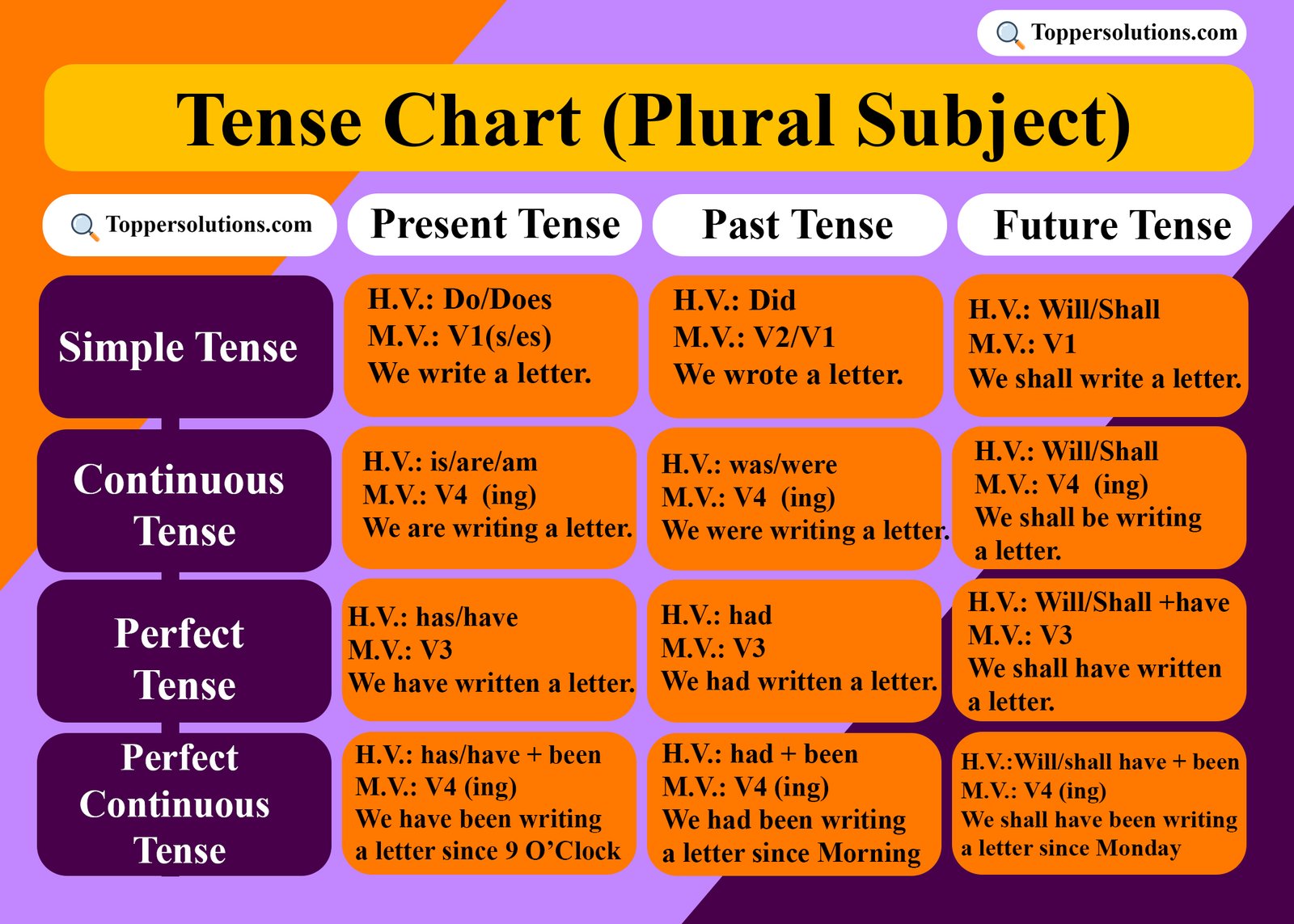
A tense chart with a Plural subject is important for several reasons, particularly in the context of language learning and effective communication.
Here is the another chart of the Tense (Plural Subject)
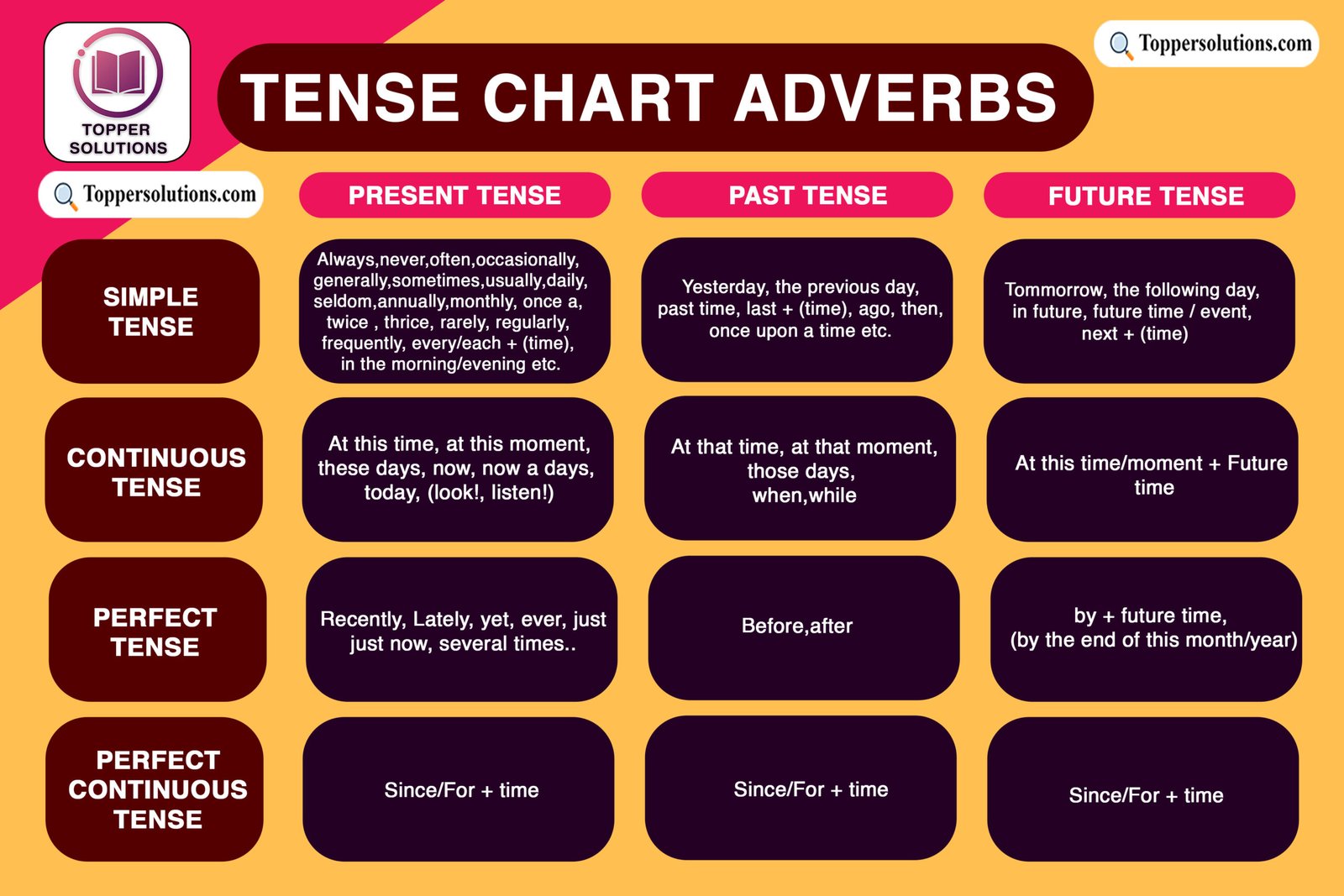
Adverbs of Tense:
Adverbs of time are words or phrases that provide information about when an action or event occurs. They answer questions such as “when,” “how often,” or “for how long.” Examples include “yesterday,” “today,” “soon,” “always,” and “in the evening.”
Here is the full chart for adverbs of time in Tenses:
Tense Examples:
Here is the chart of Tense with mixed examples;

- What are verb tenses?
Verb tenses are grammatical structures that indicate the time when an action or state of being occurs in relation to the present, past, or future.
- How many tenses are there in English?
English has three primary tenses: Present, Past, and Future. Each tense has various forms and aspects that convey different nuances of time.
- What is the difference between simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous tenses?
Simple tenses indicate straightforward actions or states. Continuous tenses emphasize ongoing actions. Perfect tenses convey completion or a point in time related to the action. Perfect continuous tenses express both duration and completion.
- How do I choose the correct tense?
Choose the tense based on when the action occurred or will occur. Consider the context, and use the tense that accurately conveys the timing of the event.
- Why is it important to use the correct tense?
Using the correct tense is crucial for clear and accurate communication. It helps avoid confusion and ensures that the listener or reader understands when an action took place.
- What is the present perfect tense used for?
The present perfect tense is used to express actions that started in the past and continue into the present, or actions that have just been completed. It often involves a connection between the past and the present.
- When do I use the past perfect tense?
The past perfect tense is used to show that one action in the past happened before another action in the past. It emphasizes the order of events.
- How is the future continuous tense formed?
The future continuous tense is formed by using “will be” + the present participle (verb + ing). It is used to express ongoing actions that will happen in the future.
- Can tenses indicate duration?
Yes, continuous and perfect continuous tenses can indicate the duration of an action. For example, present continuous (“I am working”) and present perfect continuous (“I have been working”).
- What resources can help me learn and practice verb tenses?
Grammar books, online courses, language learning apps, and practice exercises can be helpful. Engaging in conversations, reading, and writing in the language are also effective ways to reinforce tense usage.
1. What is tense?
2. How many tenses are there in English?
3. What is the difference between simple past and past perfect tense?
4. When should I use the present continuous tense?
5. Can the future tense be used to talk about plans and intentions?
6. How do I form the future perfect tense?
7. Is it possible to mix tenses in a sentence?
8. What is the difference between "will" and "going to" for expressing the future tense?
9. Can the tense of a sentence change the meaning of the sentence?
10. Are there irregular verbs that do not follow the typical tense patterns?
Your school organized a ‘Nipun Mela’ Prepare a report for the local news-paper using the given hints and your experience. (planning, model display, stalls, decoration, visit of guests, prizes) NIPUN …
अंग्रेजी पढ़ना कैसे सीखे अंग्रेजी एक वैश्विक भाषा है, और इसे सीखना आज के समय में बहुत फायदेमंद हो सकता है। यहाँ कुछ तरीके दिए गए हैं जिनसे आप अंग्रेजी …
What is a complex sentence? Definition: A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. An independent clause, also known as a …

2 thoughts on “Tense Chart In English: Types, Rules, Definitions, Formulas & Examples”